Tiger Reserves in India: India declared the Bengal Tiger as its National Animal in April 1973, replacing the lion, to highlight its importance and protect it from extinction. This decision was part of the Project Tiger initiative, launched to save endangered species listed in the IUCN Red Data Book.
India set up Tiger Reserves in 1973, focusing on safeguarding their natural habitats to support tiger conservation. Today, the country has 58 tiger reserves managed under Project Tiger and monitored by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA). India is home to nearly 80% of the world’s tiger population, making these reserves crucial for the survival of this iconic species.
Tiger Reserves in India 2025
India is home to 58 tiger reserves, managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) under Project Tiger. The country hosts nearly 80% of the world’s tiger population, making these reserves vital for tiger conservation.
The tiger population in India has steadily grown over the years: 1,411 in 2006, 1,706 in 2010, 2,226 in 2014, and 2,967 in 2018, reflecting the success of conservation efforts. According to Section 38V of the Wild Life Protection Act, 1972, state governments establish tiger reserves based on NTCA recommendations. Any changes to reserve boundaries must be approved by the National Board for Wildlife, with guidance from the NTCA.
Also Check: States and Capitals of India 2025
List of Tiger Reserves in India (2025)
India has 58 tiger reserves across various states, home to nearly 80% of the world’s tiger population. These reserves are managed under Project Tiger by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA). The following is the complete list with their locations and year of establishment:
| S. No. | Tiger Reserve Name | State/UT | Region | Year Established |
| 1 | Bandipur | Karnataka | Western Ghats | 1974 |
| 2 | Corbett | Uttarakhand | Himalayan Foothills | 1973 |
| 3 | Kanha | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 1974 |
| 4 | Manas | Assam | Eastern Himalayas | 1973 |
| 5 | Melghat | Maharashtra | Satpura Range | 1974 |
| 6 | Palamu | Jharkhand | Chota Nagpur | 1973 |
| 7 | Ranthambore | Rajasthan | Aravalli Range | 1973 |
| 8 | Simlipal | Odisha | Eastern Ghats | 1973 |
| 9 | Sunderban | West Bengal | Sundarbans | 1984 |
| 10 | Periyar | Kerala | Western Ghats | 1978 |
| 11 | Sariska | Rajasthan | Aravalli Range | 1978 |
| 12 | Buxa | West Bengal | Eastern Himalayas | 1983 |
| 13 | Indravati | Chhattisgarh | Bastar Plateau | 1982 |
| 14 | Namdapha | Arunachal Pradesh | Eastern Himalayas | 1983 |
| 15 | Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam | Telangana | Deccan Plateau | 1983 |
| 16 | Dudhwa | Uttar Pradesh | Terai | 1987 |
| 17 | Kalakad Mundanthurai | Tamil Nadu | Western Ghats | 1988 |
| 18 | Valmiki | Bihar | Gangetic Plains | 1990 |
| 19 | Pench (Madhya Pradesh) | Madhya Pradesh | Satpura | 1992 |
| 20 | Tadoba Andhari | Maharashtra | Central India | 1993 |
| 21 | Bandhavgarh | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 1993 |
| 22 | Panna | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 1994 |
| 23 | Dampa | Mizoram | Mizo Hills | 1994 |
| 24 | Bhadra | Karnataka | Western Ghats | 1998 |
| 25 | Pench (Maharashtra) | Maharashtra | Satpura Range | 1999 |
| 26 | Pakke | Arunachal Pradesh | Eastern Himalayas | 2002 |
| 27 | Nameri | Assam | Eastern Himalayas | 1999 |
| 28 | Satpura | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 1999 |
| 29 | Anamalai | Tamil Nadu | Western Ghats | 2008 |
| 30 | Udanti-Sitanadi | Chhattisgarh | Maikal Hills | 2008 |
| 31 | Satkosia | Odisha | Eastern Ghats | 2007 |
| 32 | Kaziranga | Assam | Eastern Himalayas | 2007 |
| 33 | Achanakmar | Chhattisgarh | Maikal Hills | 2009 |
| 34 | Kali (formerly Dandeli-Anshi) | Karnataka | Western Ghats | 2010 |
| 35 | Sanjay Dubri | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 2011 |
| 36 | Mudumalai | Tamil Nadu | Western Ghats | 2012 |
| 37 | Nagarhole | Karnataka | Western Ghats | 2012 |
| 38 | Parambikulam | Kerala | Western Ghats | 2010 |
| 39 | Sahyadri | Maharashtra | Western Ghats | 2009 |
| 40 | Biligiri Ranganatha Temple | Karnataka | Western Ghats | 2010 |
| 41 | Kawal | Telangana | Deccan Plateau | 2012 |
| 42 | Sathyamangalam | Tamil Nadu | Western Ghats | 2013 |
| 43 | Mukundara Hills | Rajasthan | Aravalli Range | 2013 |
| 44 | Nawegaon Nagzira | Maharashtra | Central India | 2013 |
| 45 | Amrabad | Telangana | Deccan Plateau | 2014 |
| 46 | Pilibhit | Uttar Pradesh | Terai | 2014 |
| 47 | Bor | Maharashtra | Central India | 2014 |
| 48 | Rajaji | Uttarakhand | Shivalik Range | 2015 |
| 49 | Orang | Assam | Eastern Himalayas | 2016 |
| 50 | Kamlang | Arunachal Pradesh | Eastern Himalayas | 2017 |
| 51 | Srivilliputhur Megamalai | Tamil Nadu | Western Ghats | 2021 |
| 52 | Ramgarh Vishdhari | Rajasthan | Aravalli Range | 2022 |
| 53 | Guru Ghasidas | Chhattisgarh | Maikal Hills | 2023 |
| 54 | Veerangana Durgavati | Madhya Pradesh | Central India | 2023 |
| 55 | Dholpur-Karauli | Rajasthan | Aravalli Range | 2023 |
| 56 | Guru Ghasidas-Tamor Pingla | Chhattisgarh | – | 2024 |
| 57 | Ratapani | Madhya Pradesh | – | 2024 |
| 58 | Madhav | Madhya Pradesh | Gwalior-Chambal | 2025 |
Top 10 Largest Tiger Reserves in India
India’s largest tiger reserves cover vast landscapes with diverse habitats, playing a key role in tiger conservation. These reserves, spread across states like Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Assam, Odisha, and Telangana, provide safe havens for Bengal tigers and many other wildlife species.
| S. No. | Tiger Reserve | State | Total Area (sq. km.) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam | Andhra Pradesh, Telangana | 3296.31 |
| 2 | Manas National Park | Assam | 3150.92 |
| 3 | Melghat Tiger Reserve | Maharashtra | 2768.52 |
| 4 | Similipal National Park | Odisha | 2750 |
| 5 | Amrabad Tiger Reserve | Telangana | 2611.39 |
| 6 | Sundarbans Tiger Reserve | West Bengal | 2584.89 |
| 7 | Dudhwa Tiger Reserve | Uttar Pradesh | 2201.77 |
| 8 | Satpura Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh | 2133.30 |
| 9 | Namdapha Tiger Reserve | Arunachal Pradesh | 2052.82 |
| 10 | Kanha Tiger Reserve | Madhya Pradesh | 2051.79 |
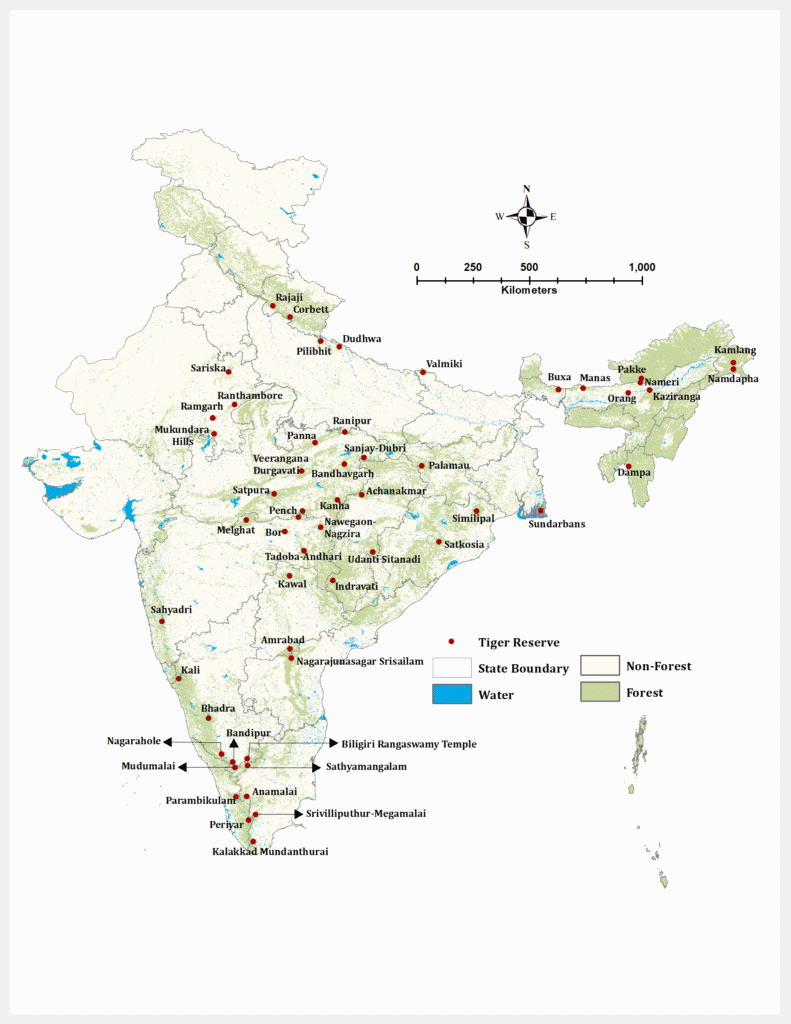
Tiger Reserves of India Map
A Tiger Reserves Map of India shows the distribution of all 58 tiger reserves across states and union territories. These reserves are crucial for protecting the endangered tiger population, with Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, and Maharashtra having the highest number of reserves.
Major Steps Taken to Save Tigers in India
India’s tiger conservation efforts are recognized worldwide for their comprehensive approach, combining policy, protection, and community participation. The following are the key initiatives:
1. Project Tiger (1973)
Launched with nine tiger reserves, Project Tiger is now active in 58 reserves. It aims to maintain viable tiger populations through scientific habitat management and strict protection measures.
2. Strong Legal Framework
The Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 was strengthened, and the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) was established in 2006 to oversee tiger reserves and ensure effective management.
3. Expanding and Connecting Habitats
New reserves have been created in ecologically suitable areas, core and buffer zones have been expanded, and wildlife corridors restored to maintain genetic diversity among tiger populations.
4. Anti-Poaching Measures
The Special Tiger Protection Force (STPF), along with advanced surveillance tools like camera traps and aircraft, helps track tigers and prevent poaching. Intelligence networks also support law enforcement.
5. Reducing Human-Wildlife Conflict
Local communities are engaged through awareness programs, compensation for livestock loss, and other initiatives to ensure harmonious coexistence near tiger habitats.
6. Combating Illegal Wildlife Trade
India works with national and international agencies to stop trafficking of tigers and tiger parts, imposing strict penalties and coordinating global efforts.
7. Scientific Monitoring
Periodic All India Tiger Estimation and technologies like long-term camera trapping help monitor populations, track movements, and assess habitat health.
8. NGO and International Collaboration
Partnerships with NGOs, local communities, and global organizations such as WWF and the Global Tiger Forum provide resources, expertise, and support for tiger conservation.
Tiger Reserves in India 2025 FAQs
Q.1. What are tiger reserves in India?
Ans. Tiger reserves are protected areas designated to conserve tigers and their habitats under Project Tiger, managed by the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA).
Q.2. How many tiger reserves are there in India in 2025?
Ans. As of 2025, India has 58 tiger reserves spread across various states and union territories.
Q.3. Which is the largest tiger reserve in India?
Ans. Nagarjunsagar-Srisailam Tiger Reserve in Andhra Pradesh and Telangana is the largest, covering 3,296.31 sq. km.
Q.4. How has India’s tiger population changed over the years?
Ans. India’s tiger population has steadily grown: 1,411 in 2006, 1,706 in 2010, 2,226 in 2014, and 2,967 in 2018, showing the success of conservation efforts.
Q.5. What major steps are taken to protect tigers in India?
Ans. Key measures include Project Tiger, anti-poaching patrols, habitat expansion, wildlife corridors, reducing human-wildlife conflict, combating illegal trade, scientific monitoring, and NGO collaborations.









